이 글은 안드로이드를 기반으로 생각하고 내용을 정리한 글이다.
MVP 패턴
MVP 패턴은 Model, View, Presenter의 앞자리를 딴 MVC 패턴에서 파생된 패턴으로, 컨트롤러 대신 프레젠터가 존재한다.
MVC 패턴에서는 뷰/컨트롤러에서 모델에 접근해 데이터를 가져와 어떻게 표현할지 정했지만, MVP 패턴에서는 아래와 같이 책임을 분리해서 사용한다.
Model : UI와 독립적인 데이터 구조로써 데이터, 비즈니스 로직, 규칙들을 직접적으로 다룬다. 즉, 프레젠터에서 어떤 값을 요청했을 때 그 값에 맞는 정보를 반환하거나 데이터를 저장하는 등의 역할을 한다.
View : 단순히 프레젠터에서 받은 값을 표현해주고 사용자의 액션 (버튼 클릭 등)에만 관여한다.
Presenter : 프레젠터는 모델과 뷰를 알고 있기 때문에 특정 메소드를 호출하여 UI에 표시하는데 필요한 작업을 진행한다. 즉, 뷰에서 전달받은 입력값이 올바르다면 모델에서 입력값에 맞는 데이터를 받아 뷰의 정보를 표현해주는 메소드에 정상값을 전달하고, 그렇지 않다면 뷰에서 에러를 처리하는 메소드에 에러값을 전달할 수 있다.
- MVP 패턴은 뷰에서 모델이 어떤 값을 가지고 있는지는 알 필요가 없으며, 뷰에는 여러 개의 프레젠터가 존재할 수 있고, 프레젠터에도 여러개의 뷰가 존재할 수 있다.
- 하나의 뷰에서 여러 모델을 사용해서 화면에 표현하고자 할 때 (뷰에 여러개의 프레젠터가 존재할 수 있다.)
- 다수의 뷰에서 하나의 모델을 이용해 각 화면에 표현하고자 할 때 (프레젠터에 여러개의 뷰가 존재할 수 있다.)
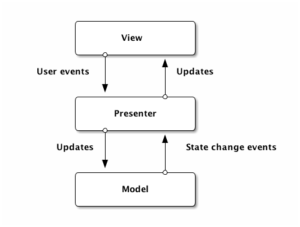
MVP의 구조는 아래와 같다.
![mvp-300x227-1]()
- 유저가 뷰에서 버튼 클릭 이벤트를 발생해 프레젠터에 값을 전달한다.
- 프레젠터는 입력값을 모델에 전달한다. (저장, 삭제, 수정 등이 될 수 있음)
- 모델은 입력값을 확인하고 데이터를 업데이트하거나 반환한다.
- 프레젠터는 모델에서 받은 값을 이용해 뷰에게 전달한다.
- 뷰와 프레젠터는 인터페이스로 통신하며, 프레젠터와 모델도 인터페이스로 통신을 한다.
장점
- 뷰와 모델이 서로 의존성이 없기 때문에 뷰가 변경되더라도 같은 값을 사용한다면 모델을 변경하지 않아도 된다.
- 모델에 기능이 추가되더라도 뷰에서 그 기능에 해당하는 UI만 만들어 표현해주면 된다.
- 서로 분리되어 있기 때문에 단위 테스트(Unit Test)가 쉬워진다.
- JUnit, Mockito 등을 이용
단점
- 프레젠터는 뷰로부터 데이터를 받아 모델의 값을 업데이트하거나 표현해주기 위한 코드로 구현되는데, 뷰에서 표현하고자 하는 값이 많아질수록 프레젠터는 커질 수밖에 없다.
예시
- 클래스명이나 파일명은 임의로 작성했다. 실제 앱에서는 더 명확한 의미의 이름들이 필요할 것 같다.
- 액티비티와 프레젠터에 인터페이스를 상속받고 서로 통신할 수 있도록 구현했다.
- 프레젠터에는 뷰와 모델을 생성자로 받는다.
메인 레이아웃
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edit_username"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginEnd="4dp"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@+id/btn_search"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_search"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="검색"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_username_string"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="이름 : "
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.415"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/edit_username" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_username"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#A2A2A2"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.104"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@+id/text_username_string"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/edit_username"
tools:text="AAAA" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_age_string"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="나이 : "
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.415"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/text_username_string" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_age"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#A2A2A2"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.104"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@+id/text_age_string"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/text_username_string"
tools:text="AAAA" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
메인 인터페이스
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
package com.example.mvp
interface MainContract {
interface View {
fun showUser(userInfo: UserInfo)
fun error(msg: String)
}
interface Presenter {
fun addUser(userInfo: UserInfo)
fun findUser(username: String)
}
}
프레젠터와 모델 사이의 인터페이스
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
package com.example.mvp
interface UserRepository {
fun addUser(userInfo: UserInfo)
fun findUser(username: String): UserInfo?
}
유저 정보와 관련된 데이터 클래스
1
2
3
4
5
6
package com.example.mvp
data class UserInfo(
val username: String,
val age: Int
)
유저 리스트 모델
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
package com.example.mvp
class UserListModel : UserRepository {
private val userList = mutableListOf<UserInfo>()
override fun addUser(userInfo: UserInfo) {
userList.add(userInfo)
}
override fun findUser(username: String): UserInfo? {
return userList.find { it.username == username }
}
}
프레젠터
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
package com.example.mvp
class MainPresenter(
private val model: UserRepository,
private val view: MainContract.View
) : MainContract.Presenter {
override fun addUser(userInfo: UserInfo) {
model.addUser(userInfo)
}
override fun findUser(username: String) {
val userInfo = model.findUser(username)
if (userInfo == null) {
view.error("유저를 찾을 수 없습니다.")
} else {
view.showUser(userInfo)
}
}
}
메인 액티비티
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
package com.example.mvp
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import android.os.Bundle
import android.widget.Button
import android.widget.EditText
import android.widget.TextView
import android.widget.Toast
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity(), MainContract.View {
private lateinit var editUserName: EditText
private lateinit var btnSearch: Button
private lateinit var textUsername: TextView
private lateinit var textAge: TextView
private lateinit var presenter: MainContract.Presenter
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
presenter = MainPresenter(UserListModel(), this)
presenter.addUser(UserInfo("AAAA", 10))
presenter.addUser(UserInfo("BBBB", 20))
presenter.addUser(UserInfo("CCCC", 30))
presenter.addUser(UserInfo("DDDD", 40))
editUserName = findViewById(R.id.edit_username)
btnSearch = findViewById(R.id.btn_search)
textUsername = findViewById(R.id.text_username)
textAge = findViewById(R.id.text_age)
btnSearch.setOnClickListener {
presenter.findUser(editUserName.text.toString())
}
}
override fun showUser(userInfo: UserInfo) {
textUsername.text = userInfo.username
textAge.text = userInfo.age.toString()
}
override fun error(msg: String) {
Toast.makeText(this, msg, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
textUsername.text = "알 수 없음"
textAge.text = "알 수 없음"
}
}
- 위 코드는 아래와 같은 구조로 작성되어 있다.
- 메인 액티비티(뷰)에서는 프레젠터로 값을 요청하고 프레젠터는 값을 받아 모델에 전달한다.
- 모델에서는 해당 값을 토대로 정보를 프레젠터로 반환하거나 추가한다.
- 프레젠터는 모델에서 받은 값을 이용해 뷰의 인터페이스를 통해 전달한다.
- 뷰는 프레젠터에서 받은 값을 이용해 화면에 표현한다.
참고
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Model-view-presenter
- https://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/모델-뷰-프리젠터
- https://www.baeldung.com/mvc-vs-mvp-pattern
Comments powered by Disqus.