MVC 패턴
이 글은 안드로이드를 기반으로 생각하고 내용을 정리한 글이다.
- MVC와 MVP 패턴을 이해하려면 먼저 왜 이러한 아키텍처 패턴을 써야하는지 알아야 한다.
아키텍처 패턴
위키에 따르면 아키텍처 패턴을 아래와 같이 정의하고 있다.
1
아키텍처 패턴(architectural pattern)은 주어진 문맥 안에서 소프트웨어 아키텍처의 공통적인 발생 문제에 대한 일반적인, 재사용 가능한 해결책을 의미한다.
- 건물을 지을 때 어떤 방식으로 지을 것인지 고민하는 것처럼 소프트웨어를 개발할 때에도 어떤 방식으로 개발을 진행해야 고민해야 하는데, 이러한 고민을 해결하기 위해 아키텍처 패턴이라는 것이 등장했다.
- 한 건물에 여러가지의 방식을 선택하면 관리하기 힘든것처럼 소프트웨어에서도 마찬가지이므로 되도록 한가지 방식을 이용해 개발하는것이 유리하다.
- 이렇게되면 다른 소프트웨어를 개발할 때에도 비슷한 경우일 때 동일한 방식을 사용할 수 있으므로 재사용성이 높아지게 되며, 개발 도중에 새로운 관리자나 개발자가 참여하더라도 어떤 패턴으로 개발이 되었는지를 알 수 있다면 개발하는데 필요한 비용(시간, 노력 등)이 줄어들 수 있는 이점이 있기 때문에 명확히 정의된 아키텍처가 중요하다.
MVC 패턴
- MVC 패턴은 Model, View, Controller의 앞자리를 따온 것으로 MVP, MVVM 등의 아키텍처 패턴에 기초가 되었다.
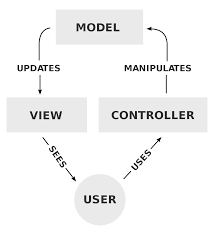
MVC 패턴은 아래와 같은 책임으로 분리한다.
- Model : UI와 독립적인 데이터 구조로써 데이터, 비즈니스 로직, 규칙들을 직접적으로 다룬다.
- View : 텍스트, 체크박스 등의 사용자 UI를 나타낸다.
- Controller : 데이터와 비즈니스 로직 사이의 상호동작을 관리한다. 즉, 사용자의 입력을 받고 처리하는 것을 담당한다.
![mvc]()
![mvc2]()
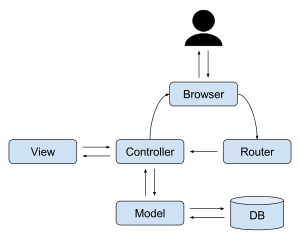
위 사진을 보면 MVC 패턴에는 여러가지 구현 방법이 존재한다는 것을 알 수 있으며, 첫 번째 사진은 MVC의 기본 모습이고 두 번째는 웹에서 사용하는 MVC 패턴(Spring Framework)이다. 뭔가 웹에서 사용하는 MVC 패턴은 MVP와 비슷해 보이는 느낌이 강한 것 같다.
안드로이드에서는 View와 Controller가 같이 존재한다고 볼 수 있기 때문에 View/Controller -> Model을 참조하게 된다.
- 안드로이드가 아닌 자바 기반의 MVC 패턴은 아래와 같다고 한다.
- MVC 패턴 (tutorialspoint)
위 글을 보니까 더 헷갈리는 거 같기도하고…
장점
- 가장 단순한 구조여서 규모가 크지 않은 프로젝트를 진행할 때 사용될 수 있으며 개발 시간이 짧다.
- 모델에는 비즈니스 로직을 구현하고 뷰에서는 모델에서 가져다 표현해주기만 하면 되기 때문
단점
- View/Controller와 Model이 밀접하게 연결되어 있어서 View/Controller의 단위 테스트(Unit Test)가 힘들다는 단점이 있다.
- 의존성이 높기 때문에 어플리케이션이 커질수록 복잡하고 유지보수가 어려워질 수 있다.
예시
레이아웃 코드
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edit_username"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginEnd="4dp"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@+id/btn_search"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_search"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="검색"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_username_string"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="이름 : "
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.415"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/edit_username" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_username"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#A2A2A2"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.104"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@+id/text_username_string"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/edit_username"
tools:text="AAAA" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_age_string"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="나이 : "
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.415"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/text_username_string" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_age"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#A2A2A2"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.104"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@+id/text_age_string"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/text_username_string"
tools:text="AAAA" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
유저 정보 데이터 클래스
1
2
3
4
5
6
package com.example.mvc
data class UserInfo(
val username: String,
val age: Int
)
모델
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
package com.example.mvc
class UserListModel {
private val userList = mutableListOf<UserInfo>()
fun addUser(userInfo: UserInfo) {
userList.add(userInfo)
}
fun findUser(username: String): UserInfo? {
return userList.find { it.username == username }
}
}
메인 액티비티
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
package com.example.mvc
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import android.os.Bundle
import android.widget.Button
import android.widget.EditText
import android.widget.TextView
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private lateinit var editUserName: EditText
private lateinit var btnSearch: Button
private lateinit var textUsername: TextView
private lateinit var textAge: TextView
private val userListModel = UserListModel()
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
userListModel.addUser(UserInfo("AAAA", 10))
userListModel.addUser(UserInfo("BBBB", 20))
userListModel.addUser(UserInfo("CCCC", 30))
userListModel.addUser(UserInfo("DDDD", 40))
editUserName = findViewById(R.id.edit_username)
btnSearch = findViewById(R.id.btn_search)
textUsername = findViewById(R.id.text_username)
textAge = findViewById(R.id.text_age)
btnSearch.setOnClickListener {
val user = userListModel.findUser(editUserName.text.toString())
if (user == null) {
textUsername.text = "알 수 없음"
textAge.text = "알 수 없음"
} else {
textUsername.text = user.username
textAge.text = user.age.toString()
}
}
}
}
- 메인 액티비티의 버튼을 살펴보면 모델인
UserListModel을 직접 호출하고 값을 가져오는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
완성화면
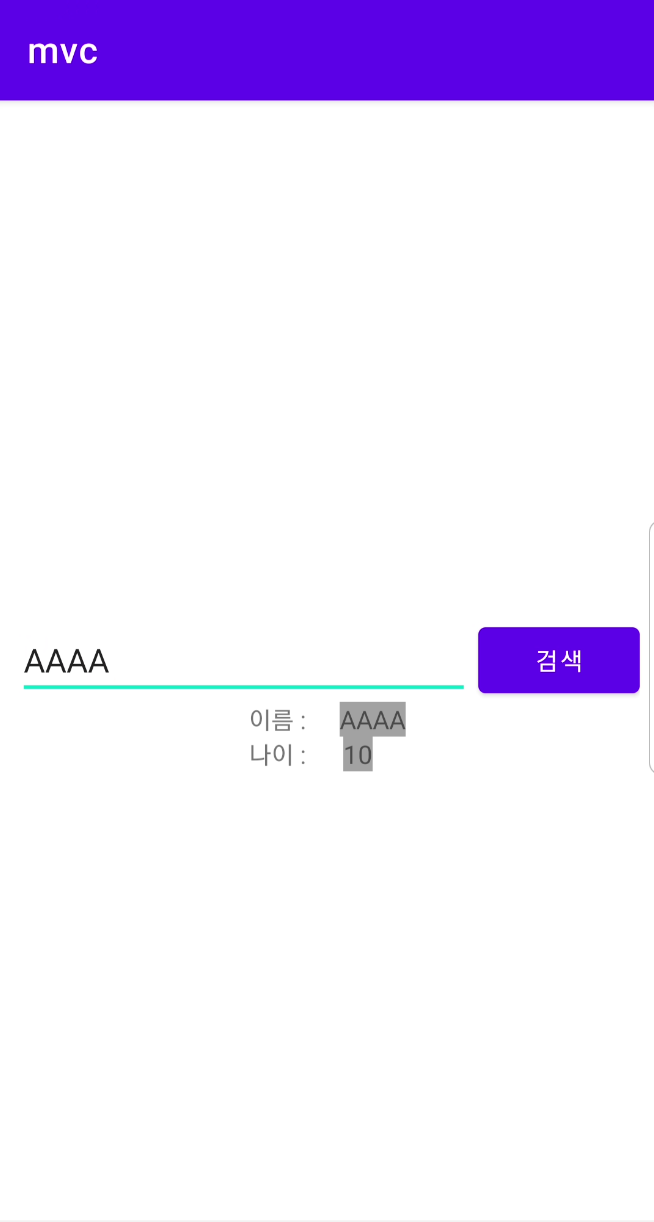
- 참고
- https://www.redhat.com/architect/5-essential-patterns-software-architecture
- https://developer.mozilla.org/ko/docs/Glossary/MVC
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Model-view-controller
- https://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/모델-뷰-컨트롤러
- https://www.baeldung.com/mvc-vs-mvp-pattern
- https://www.tutorialspoint.com/design_pattern/mvc_pattern.htm
Comments powered by Disqus.